Good Vs Bad Poker Hands
The infamous Deuce Seven off suit is known as the lowliest hand in all of holdem, and for good reason. It rates the worst of any hand in the game against a table full of random opponents. Some players will claim hands like 3 5 are worse, because when you input 2 7 and 3 5 into a poker hand calculator, the 2 7 actually rates higher. Poker hands from highest to lowest 1. Royal flush A, K, Q, J, 10, all the same suit. Straight flush Five cards in a sequence, all in the same suit.

Hand Guide: Preflop > Flop > Turn > River
Preflop Planning is an excellent guide on how to think before the flop when deciding whether to fold, call or raise based on your position and starting hand. It's the perfect compliment to this article.
Preflop overview.
Before the flop is where it all starts, where you are forced to make your first important decision depending on all of the variables involved with the hand. It is important to make good, solid decisions before the flop, as it will form the foundations for how the rest of the hand will be played out.
If you make a high-quality decision before the flop, you will set the tone for the rest of the hand and give yourself the best opportunity to get into a moneymaking position. However, if you make a bad decision before the flop, you may well set yourself up for a big loss by getting yourself into a sticky position or missing out on a potentially rewarding hand.
Start as you mean to go on in every hand. Make quality plays at the beginning and continue throughout the rest of the hand.
Therefore after you have been dealt your cards preflop, it is important to take your time to evaluate all of the different variables in the hand, and not just make decisions on the cards that you are holding. It is important to consider your position and the type of opponents you are playing against, as well as know the correct starting hand requirements. So make sure you think very carefully before every flop and build the foundations for a profitable hand by making the correct preflop strategy decision.
Preflop starting hand selection.
Choosing which hands to play and which hands to fold is fundamental to playing a winning poker game. The best hands to play in Texas Holdem are:
- Big pocket pairs: AA-TT
- Big suited connectors: AK, AQ, AJ, KQ
- Big connectors: AK, AQ, AJ, KQ
These particular combinations of cards have the best chances of winning than other cards, so if you stick to these you will find yourself in more profitable situations after the flop. It is possible to play other combinations of cards successfully, but if you are a beginner player then it is advised to stick with the big cards until you find your feet at the poker table.
Preflop position strategy.
Your position in the hand is an incredibly important variable that you should be aware of in every hand, yet it is something that is all too often forgotten about.
The dynamics of play are slightly different in the preflop betting round, as the small and big blind will be last to act, whereas they will be the first to act on every other betting round. However, the general principles of position will remain the same, as you want to try and play more hands where you have position over your opponents than in positions where you do not.
This means that you should avoid playing too many hands in the blinds or in an early position, as being one of the first to act in each hand can make things very difficult unless you are holding a premium hand. Be very careful when playing in the blinds, and don’t feel as though you have to enter more pots in these positions because you have already committed money to the pot. It is far safer to let marginal hands go rather than to call raises with half a holding and play out of position for the rest of the hand.
Your position can often play a more influential role than the strength of the cards that players are actually holding, so try and keeping the upper hand by combining good position with good cards.
The cards listed above in the starting hands selection section can be played from almost any position, but you should try and tighten up your starting hand selection in the earlier positions. So as a general rule, you can play with a wider range of the top starting hands in later positions than you should in the earlier positions in the hand.
So the top strategy tips on preflop position are:
- Always be aware of your position in a hand
- Try to avoid playing out of position unless you have a strong holding
- You can afford to loosen up your starting hand requirements in later positions
- Don’t feel committed to playing hands when in the blinds
Preflop betting tips.
When the action reaches you before the flop, you will be faced with the decision to either fold, call or raise. If there has been no raise before you, then a call will simply mean matching the size of the big blind, which is also known as ‘limping in’. This is generally not a good play, as if you are entering any pot in Holdem you will want to be making a raise and show aggression.
If you are limping in with a hand, you are either entering the pot with a sub-standard hand or you are playing a premium hand too weakly. So the real question you should ask yourself if you are first to enter the pot before the flop is; “Am I folding or am I raising?”
The majority of the time you should either 'pump it' or 'dump it'. Avoid limping in by simply calling the big blind.
Preflop bet sizing.
If you decide that you are going to enter the pot, you should be looking to make a raise of about 3 or 4 times the size of the big blind. By making a minimum raise you are letting opponents with marginal hands come in cheaply, and you are almost defeating the object of making a preflop raise.
The idea of a preflop raise is to reduce the amount of players who follow you to see a flop, as it is easier to make profitable decisions when there are fewer players in the pot. So make sure to come in with a strong 3 or 4 BB raise, and increase the size of the raise if you find that a lot of players are still calling these raises with marginal hands or if other players have limped in before you.
If there has been a raise before you, you must now consider whether you should fold, call or raise. If you have a poor or marginal starting hand you should look to fold. If you have a good starting hand like the ones mentioned above you should be happy to call and see a flop. If you have one of the top starting hands like AA or KK, should re-raise to help try and get as much money into the pot as possible.
Limping in.
There will be a few cases where limping-in will be an acceptable play. This will normally be when there have been a number of other players limping-in before you, and so you will have better odds to see a flop.
The best hands to limp in with are strong drawing hands such as suited cards with an ace or king, or any connecting cards that can make a straight. You are not looking to make top pair in these limped multi-way pots, as they can often land you in trouble. So aim to play hands that can land you a very strong holding or a strong draw, and then comfortably fold on the flop if neither of these materialize.
Top strategy tips for preflop betting:
- Don’t be afraid to bet or raise
- Make solid 3 or 4 BB raises when entering an un-opened pot
- Increase the size of your raise if other players have limped or are calling stations
- Avoid limping with mediocre hands
- Only limp if you have a potentially strong hand and others have limped before you
Other preflop strategy tips.
If you are playing in a shorthanded game such as a 6-max table, you can afford to reduce your starting hand requirements so that you can see more flops. If you stick to the starting hand requirements mentioned above, you would probably find that you are folding too often and missing out on opportunities to win money. So you can afford to play other hands such as AT, KJ, KT, QJ and so on.
When making your decision pre flop, you should also consider the type of players who you are playing against. If you notice that a tight player has made a raise, it is likely that they have a very strong hand, so you should re-evaluate the strength of your cards in this hand. Similarly, if a loose player makes a raise, it is more likely to be profitable to be call with a decent hand as you could well be holding a stronger hand than them.
It is important to not be afraid about making bets or raises before the flop. It is important to be aggressive in poker, as it is a winning style that all good players adopt. If you are afraid to make bets and raises when you should be, then you will be making unprofitable decisions and you will find it hard to ever win money from the game. To help accustom yourself to being aggressive, you could try dropping down in limits where there is less money at stake, so that you can become comfortable with playing aggressively and notice the advantages of an aggressive style over a weak playing style.
Useful preflop strategy articles:
- Starting Hand Selection (Beginner)
- Position (Beginner)
- The Gap Concept (Intermediate)
- Relative Position (Advanced)
Go back to the thorough hand guide.
In our poker math and probability lesson it was stated that when it comes to poker; “the math is essential“. Although you don’t need to be a math genius to play poker, a solid understanding of probability will serve you well and knowing the odds is what it’s all about in poker. It has also been said that in poker, there are good bets and bad bets. The game just determines who can tell the difference. That statement relates to the importance of knowing and understanding the math of the game.
In this lesson, we’re going to focus on drawing odds in poker and how to calculate your chances of hitting a winning hand. We’ll start with some basic math before showing you how to correctly calculate your odds. Don’t worry about any complex math – we will show you how to crunch the numbers, but we’ll also provide some simple and easy shortcuts that you can commit to memory.
Basic Math – Odds and Percentages
Odds can be expressed both “for” and “against”. Let’s use a poker example to illustrate. The odds against hitting a flush when you hold four suited cards with one card to come is expressed as approximately 4-to-1. This is a ratio, not a fraction. It doesn’t mean “a quarter”. To figure the odds for this event simply add 4 and 1 together, which makes 5. So in this example you would expect to hit your flush 1 out of every 5 times. In percentage terms this would be expressed as 20% (100 / 5).
Here are some examples:
- 2-to-1 against = 1 out of every 3 times = 33.3%
- 3-to-1 against = 1 out of every 4 times = 25%
- 4-to-1 against = 1 out of every 5 times= 20%
- 5-to-1 against = 1 out of every 6 times = 16.6%
Converting odds into a percentage:
- 3-to-1 odds: 3 + 1 = 4. Then 100 / 4 = 25%
- 4-to-1 odds: 4 + 1 = 5. Then 100 / 5 = 20%
Converting a percentage into odds:
- 25%: 100 / 25 = 4. Then 4 – 1 = 3, giving 3-to-1 odds.
- 20%: 100 / 20 = 5. Then 5 – 1 = 4, giving 4-to-1 odds.
Another method of converting percentage into odds is to divide the percentage chance when you don’t hit by the percentage when you do hit. For example, with a 20% chance of hitting (such as in a flush draw) we would do the following; 80% / 20% = 4, thus 4-to-1. Here are some other examples:
- 25% chance = 75 / 25 = 3 (thus, 3-to-1 odds).
- 30% chance = 70 / 30 = 2.33 (thus, 2.33-to-1 odds).
Some people are more comfortable working with percentages rather than odds, and vice versa. What’s most important is that you fully understand how odds work, because now we’re going to apply this knowledge of odds to the game of poker.
The right kind of practice between sessions can make a HUGE difference at the tables. That’s why this workbook has a 5-star rating on Amazon and keeps getting reviews like this one: “I don’t consider myself great at math in general, but this work is helping things sink in and I already see things more clearly while playing.”
Instant Download · Answer Key Included · Lifetime Updates
Counting Your Outs
Before you can begin to calculate your poker odds you need to know your “outs”. An out is a card which will make your hand. For example, if you are on a flush draw with four hearts in your hand, then there will be nine hearts (outs) remaining in the deck to give you a flush. Remember there are thirteen cards in a suit, so this is easily worked out; 13 – 4 = 9.
Another example would be if you hold a hand like and hit two pair on the flop of . You might already have the best hand, but there’s room for improvement and you have four ways of making a full house. Any of the following cards will help improve your hand to a full house; .
Good Vs Bad Poker Hands Held
The following table provides a short list of some common outs for post-flop play. I recommend you commit these outs to memory:
Good Vs Bad Poker Hands
Table #1 – Outs to Improve Your Hand
The next table provides a list of even more types of draws and give examples, including the specific outs needed to make your hand. Take a moment to study these examples:
Table #2 – Examples of Drawing Hands (click to enlarge)
Counting outs is a fairly straightforward process. You simply count the number of unknown cards that will improve your hand, right? Wait… there are one or two things you need to consider:
Don’t Count Outs Twice
There are 15 outs when you have both a straight and flush draw. You might be wondering why it’s 15 outs and not 17 outs, since there are 8 outs to make a straight and 9 outs for a flush (and 8 + 9 = 17). The reason is simple… in our example from table #2 the and the will make a flush and also complete a straight. These outs cannot be counted twice, so our total outs for this type of draw is 15 and not 17.
Anti-Outs and Blockers
There are outs that will improve your hand but won’t help you win. For example, suppose you hold on a flop of . You’re drawing to a straight and any two or any seven will help you make it. However, the flop also contains two hearts, so if you hit the or the you will have a straight, but could be losing to a flush. So from 8 possible outs you really only have 6 good outs.
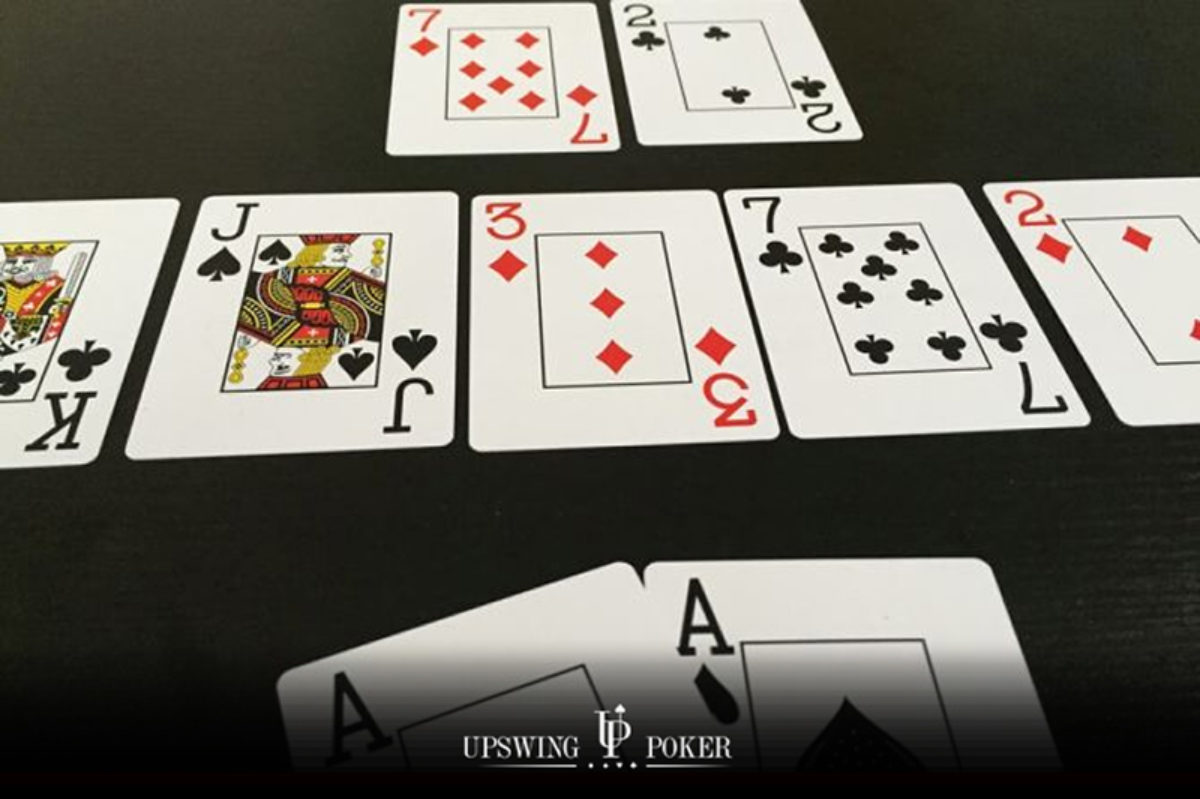

It’s generally better to err on the side of caution when assessing your possible outs. Don’t fall into the trap of assuming that all your outs will help you. Some won’t, and they should be discounted from the equation. There are good outs, no-so good outs, and anti-outs. Keep this in mind.
Calculating Your Poker Odds
Once you know how many outs you’ve got (remember to only include “good outs”), it’s time to calculate your odds. There are many ways to figure the actual odds of hitting these outs, and we’ll explain three methods. This first one does not require math, just use the handy chart below:
Table #3 – Poker Odds Chart
As you can see in the above table, if you’re holding a flush draw after the flop (9 outs) you have a 19.1% chance of hitting it on the turn or expressed in odds, you’re 4.22-to-1 against. The odds are slightly better from the turn to the river, and much better when you have both cards still to come. Indeed, with both the turn and river you have a 35% chance of making your flush, or 1.86-to-1.
We have created a printable version of the poker drawing odds chart which will load as a PDF document (in a new window). You’ll need to have Adobe Acrobat on your computer to be able to view the PDF, but this is installed on most computers by default. We recommend you print the chart and use it as a source of reference. It should come in very handy.
Doing the Math – Crunching Numbers
There are a couple of ways to do the math. One is complete and totally accurate and the other, a short cut which is close enough.
Let’s again use a flush draw as an example. The odds against hitting your flush from the flop to the river is 1.86-to-1. How do we get to this number? Let’s take a look…
With 9 hearts remaining there would be 36 combinations of getting 2 hearts and making your flush with 5 hearts. This is calculated as follows:
(9 x 8 / 2 x 1) = (72 / 2) ≈ 36.
This is the probability of 2 running hearts when you only need 1 but this has to be figured. Of the 47 unknown remaining cards, 38 of them can combine with any of the 9 remaining hearts:
9 x 38 ≈ 342.
Now we know there are 342 combinations of any non heart/heart combination. So we then add the two combinations that can make you your flush:
36 + 342 ≈ 380.
The total number of turn and river combos is 1081 which is calculated as follows:
(47 x 46 / 2 x 1) = (2162 / 2) ≈ 1081.
Now you take the 380 possible ways to make it and divide by the 1081 total possible outcomes:
380 / 1081 = 35.18518%
This number can be rounded to .352 or just .35 in decimal terms. You divide .35 into its reciprocal of .65:
Good Vs Bad Poker Hands Game
0.65 / 0.35 = 1.8571428
And voila, this is how we reach 1.86. If that made you dizzy, here is the short hand method because you do not need to know it to 7 decimal points.
The Rule of Four and Two
Good Vs Bad Poker Hands Play
A much easier way of calculating poker odds is the 4 and 2 method, which states you multiply your outs by 4 when you have both the turn and river to come – and with one card to go (i.e. turn to river) you would multiply your outs by 2 instead of 4.
Imagine a player goes all-in and by calling you’re guaranteed to see both the turn and river cards. If you have nine outs then it’s just a case of 9 x 4 = 36. It doesn’t match the exact odds given in the chart, but it’s accurate enough.
Good Vs Bad Poker Hands Challenge
What about with just one card to come? Well, it’s even easier. Using our flush example, nine outs would equal 18% (9 x 2). For a straight draw, simply count the outs and multiply by two, so that’s 16% (8 x 2) – which is almost 17%. Again, it’s close enough and easy to do – you really don’t have to be a math genius.
Do you know how to maximize value when your draw DOES hit? Like…when to slowplay, when to continue betting, and if you do bet or raise – what the perfect size is? These are all things you’ll learn in CORE, and you can dive into this monster course today for just $5 down…
Conclusion
In this lesson we’ve covered a lot of ground. We haven’t mentioned the topic of pot odds yet – which is when we calculate whether or not it’s correct to call a bet based on the odds. This lesson was step one of the process, and in our pot odds lesson we’ll give some examples of how the knowledge of poker odds is applied to making crucial decisions at the poker table.
As for calculating your odds…. have faith in the tables, they are accurate and the math is correct. Memorize some of the common draws, such as knowing that a flush draw is 4-to-1 against or 20%. The reason this is easier is that it requires less work when calculating the pot odds, which we’ll get to in the next lesson.
Related Lessons

By Tom 'TIME' Leonard
Tom has been writing about poker since 1994 and has played across the USA for over 40 years, playing every game in almost every card room in Atlantic City, California and Las Vegas.